Project CETI: Reinforcement Learning-Based Framework for Whale Rendezvous via Autonomous Sensing Robots
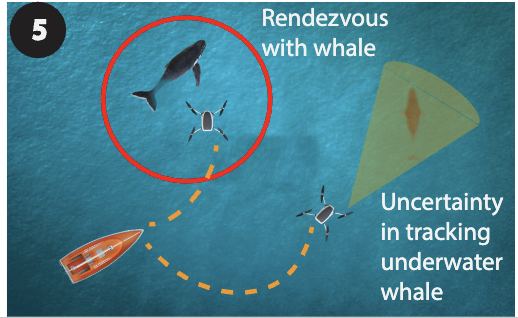
In this paper, we propose an algorithmic framework that co-develops multi-agent reinforcement learning–based routing (autonomy module) and Synthetic Aperture Radar-based Very High Frequency (VHF) signal-based bearing estimation (sensing module) for maximizing rendezvous opportunities of autonomous robots with sperm whales. The sensing module is compatible with low-energy VHF tags, commonly used for tracking wildlife. The autonomy module leverages in-situ noisy bearing measurements of whale vocalizations, VHF tags, and whale dive behaviors to enable time–critical rendezvous of a robot team with multiple whales in simulation. We conduct experiments at sea in the native habitat of sperm whales using an “engineered whale” – a speedboat equipped with a VHF-emitting tag, emulating five distinct whale tracks, with different whale motions. The sensing module shows a median bearing error of 10.55 degrees to the tag.
Citation
- Reinforcement Learning-Based Framework for Whale Rendezvous via Autonomous Sensing Robots
, Sushmita Bhattacharya Ninad Jadhav, Daniel Vogt, Yaniv Aluma, Pernille Tonessen, Akarsh Prabhakara, Swarun Kumar, Shane Gero, Robert J. Wood, and Stephanie Gil, Science Robotics 2024
